Greenhouse Design: Creating an Ideal Growing Haven
Greenhouses have become essential havens for plant enthusiasts and agricultural experts alike. These controlled environments offer the perfect solution to extend growing seasons, protect plants from harsh weather conditions, and optimize crop yields. As a passionate greenhouse enthusiast and advisor, I firmly believe that a well-designed greenhouse is key to harnessing the full potential of your plants. In this article, we will explore the various considerations that go into creating an ideal greenhouse, including frame materials, cover materials, site selection, foundation, and other crucial factors. So, let’s embark on this exciting journey of greenhouse design!
Introduction
As someone deeply involved in the world of horticulture and agriculture, I understand the vital role greenhouses play in modern farming and gardening practices. These structures act as a bridge between nature’s unpredictability and our desire for optimum plant growth. However, to achieve the best results, one must carefully consider every aspect of greenhouse design.
Understanding the Importance of Greenhouse Design
The Role of Greenhouses in Modern Agriculture
In today’s fast-paced world, greenhouse cultivation has become a beacon of hope for sustainable food production. Greenhouses provide a controlled environment that allows farmers to cultivate crops throughout the year, independent of the external climate.
Maximizing Growth Potential with Smart Greenhouse Design
An efficiently designed greenhouse not only protects plants but also optimizes their growth potential. By harnessing natural resources and using smart technologies, we can create an environment where plants thrive.
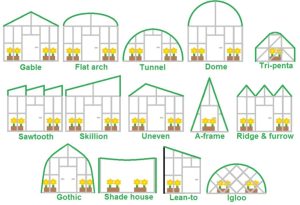
What Will Your Greenhouse Look Like?
Greenhouses come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The image below should help get your creative juices flowing.
Frame Materials: Choosing the Right Support Structure
The frame forms the backbone of any greenhouse, providing stability and support to the entire structure. Selecting the right frame material is crucial for the greenhouse’s longevity and performance.
Sturdy and Durable Options
When it comes to frame materials, there are several choices available, each with its unique advantages. Steel, aluminum, and wood are popular options due to their strength and durability. While not as sturdy, PVC is also a viable framing material.
Wood: Wood is a sturdy, attractive frame material, but it can rot in the humid environment of a greenhouse. Be sure to use a rot-resistant specie such as cedar or redwood or use pressure treated wood. It is also best suited for smaller greenhouses that utilize glass or polycarbonate panels.
Aluminum: Aluminum doesn’t rust or deteriorate when exposed to the elements, but, it’s not as strong as wood or steel. When it’s used for a greenhouse frame, the support parts either need to be made from thicker material or be doubled up. Despite its lack of strength, aluminum offers a sturdy structure for holding glass or polycarbonate panels.
Galvanized Steel: Galvanized steel is a great choice for durability without breaking the bank. It’s really strong, so you won’t need as many framing pieces in your greenhouse, resulting in fewer shadows. However, keep in mind that most steel frames are designed for polyethylene film, not solid glass or polycarbonate panels. While they’re popular for commercial growers, they might not be the most attractive option for a residential setup. One significant drawback is that the galvanizing will wear over time, leading to rusting issues down the line.
PVC Plastic Pipe: PVC plastic pipes are budget-friendly, lightweight and easy to put together. Although a frame made from PVC might not be as sturdy as metal or wood, the industry is working on designs that include metal supports along with PVC framing to improve its strength. Another advantage of PVC is that it helps retain heat better compared to metal frames. Greenhouses with PVC frames typically use polyethylene film for the walls. These are usually smaller, backyard greenhouses meant for hobbies, as PVC doesn’t work as well for larger greenhouse setups. Nowadays, most hobby greenhouse kits come with PVC frames as a popular choice.
Balancing Cost and Longevity
While sturdy materials offer reliability, it’s essential to strike a balance between cost and longevity. Assessing your budget and long-term goals can help make an informed decision
Cover Materials: Enhancing Efficiency and Insulation
The cover material directly influences light diffusion, temperature control, and overall energy efficiency within the greenhouse. Choosing the right cover material is pivotal for achieving the desired results.
Glass: Timeless Elegance and Superior Clarity
Glass offers unmatched clarity and beauty, allowing maximum sunlight penetration. However, it requires careful handling and may be expensive.
Polycarbonate: A Balance of Strength and Light Diffusion
Polycarbonate panels are known for their impact resistance and excellent light diffusion. They are a practical choice for those seeking a balance between performance and cost.
Polyethylene: Cost-Effective and Easy to Install
Polyethylene film is an affordable option that is easy to install. While it may not have the longevity of other materials, it can still be an attractive choice for seasonal use.
Site Selection: Optimizing Sunlight Exposure and More
Selecting the right location for your greenhouse is paramount to its success. Proper site selection can significantly impact the amount of sunlight your plants receive and influence the microclimate within the structure. Before you start the selection process, it’s important to think about the plants you plan to grow in your greenhouse and identify your greenhouse goals.
Finding the Perfect Location
When choosing a site, consider factors such as orientation, nearby structures, and potential shading from trees or buildings. South-facing locations are often preferred to maximize sun exposure. You also want well drained ground that is as level as possible.
Sunlight and Microclimates
Understanding the sunlight patterns and microclimates in your area can help you position the greenhouse optimally. Analyzing the sun’s path throughout the day and during different seasons is essential. If you use shade cloth, you can protect your plants from getting too much sun. If you build in a shadier area, you may limit the plants you can grow.
Wind and Ventilation Considerations
Protection from strong winds is crucial, as they can damage the greenhouse and stress the plants. Additionally, proper ventilation ensures a healthy environment and prevents heat buildup.
Foundation: Creating a Solid Base for Your Greenhouse
A sturdy and well-designed foundation provides stability to the greenhouse structure. It prevents sinking, shifting, and other structural issues over time.
Importance of a Proper Foundation
A proper foundation ensures that the greenhouse remains level and secure. It also helps with efficient water drainage, avoiding water-related problems.
Different Foundation Options
Concrete, gravel, and treated wood are common materials used for greenhouse foundations. Each option has its advantages, and the choice depends on factors such as budget and local climate.
Ventilation and Climate Control: Keeping a Healthy Environment
Maintaining proper ventilation and climate control is vital for the health of your plants. A well-ventilated greenhouse prevents excessive heat and humidity, reducing the risk of diseases.
Natural Ventilation and Heating Methods
Strategically placed vents, louvers, and roof windows enable natural airflow, promoting a healthy exchange of air within the greenhouse. If you use plastic sheeting, you can roll up the sides for ventilation on hot days.
Natural ways to provide extra heat are through thermal mass and composting. When the weather gets colder, place some water barrels in the greenhouse where they can get maximum sunlight. For a south-facing greenhouse (which is where is should be in the northern hemisphere) place the barrels just off the north wall. You can also generate extra heat by setting up compost bins in your greenhouse. You’ll want to plan for adequate space for these systems when putting together your greenhouse design,
Automated Climate Control Systems
Automated climate control systems can help regulate temperature, humidity, and even irrigation, ensuring optimal conditions for plant growth. Thermostat controlled heaters and fans can do a better job of maintaining a consistent greenhouse environment and are more labor efficient.
Irrigation and Water Management: Efficiently Nourishing Your Plants
Water is a precious resource, and efficiently managing irrigation is crucial for sustainable greenhouse operations.
Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the plant roots, minimizing water wastage and reducing the risk of foliar diseases.
Water Recycling and Rainwater Harvesting
Implementing water recycling and rainwater harvesting practices further reduce water consumption and environmental impact.
Layout and Shelving: Optimizing Space and Organization
A well-thought-out layout and proper shelving can maximize the available space and improve accessibility.
Planning the Layout for Accessibility and Functionality
Organize the interior space in a way that facilitates movement and makes daily operations more efficient.
Utilizing Vertical Space with Shelving
Vertical shelving allows you to grow more plants in a limited area, making the most of the greenhouse’s vertical space.
Automation and Technology: Embracing Smart Greenhouse Solutions
Embracing automation and technology can revolutionize greenhouse operations, enhancing productivity and resource management.
The Benefits of Automation
Automated systems can control various aspects of the greenhouse, including temperature, irrigation, and lighting, with precision and efficiency.
Integrating Technology for Improved Productivity
Utilizing smart sensors and data analysis tools can provide valuable insights into plant health and optimize growth conditions.
Sustainable Greenhouse Design
As stewards of the environment, greenhouse operators can adopt sustainable practices to minimize their impact on the planet.
Renewable Energy Sources
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar power can significantly reduce greenhouse emissions.
Eco-Friendly Materials and Practices
Choosing eco-friendly materials and implementing recycling initiatives contribute to a greener and more sustainable greenhouse operation.
Embracing smart greenhouse design practices is not just about growing plants; it’s about cultivating a greener future for generations to come. By making informed decisions regarding frame materials, cover materials, site selection, foundation, and other considerations, we can create spaces where plants thrive while treading lightly on the environment.
Conclusion
The foundation of a successful greenhouse lies in meticulous planning and thoughtful decision-making. Each aspect, from the choice of frame and cover materials to site selection and sustainable practices, plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the greenhouse.
Remember, every greenhouse is unique, and while these guidelines provide a solid starting point, tailoring the design to suit your specific needs and goals is essential. By staying open to new technologies and embracing sustainability, we can create greenhouses that not only maximize productivity but also contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the ideal location for a greenhouse?
The ideal location for a greenhouse is south-facing to maximize sunlight exposure. Additionally, it should be protected from strong winds and positioned to take advantage of microclimates.
Which cover material is best for a greenhouse?
The choice of cover material depends on various factors. Glass offers superior clarity, while polycarbonate provides a balance of strength and light diffusion. Polyethylene is a cost-effective option suitable for seasonal use.
What foundation material should I use for my greenhouse?
Foundations can be made of concrete, gravel, or treated wood. Consider factors like budget, local climate, and the greenhouse’s size when making this decision.
Are automated climate control systems worth it?
Yes, automated climate control systems are worth investing in, as they help regulate temperature, humidity, and irrigation more effectively, leading to healthier plants and improved productivity.
How can I make my greenhouse more eco-friendly?
You can make your greenhouse more eco-friendly by adopting renewable energy sources like solar power, using eco-friendly materials, and implementing recycling initiatives to reduce your carbon footprint.




